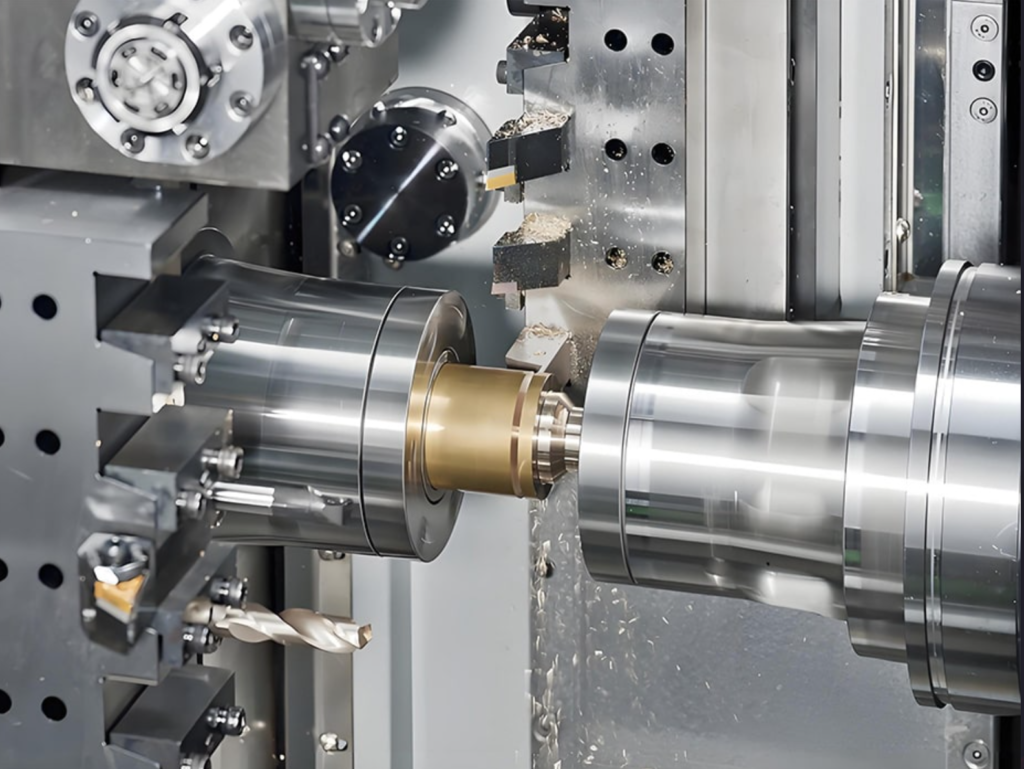
CNC machining services have evolved dramatically over the past few decades. From their early adoption in manufacturing to their integration with advanced digital technologies, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems are reshaping the way industries design, prototype, and manufacture components. As we look ahead, the future of CNC machining services appears brighter and more innovative than ever. This article explores the key trends and predictions that are set to define the next phase of growth for the CNC machining industry.
Rise of Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
One of the most significant trends transforming CNC machining services is the rise of Industry 4.0. Smart manufacturing integrates digital technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), big data analytics, and machine learning into the machining process. CNC machines are no longer isolated units but are becoming intelligent systems connected to a broader network.
These connected systems enable real-time monitoring of performance, predictive maintenance, and automation of workflows. With sensors embedded into machines, manufacturers can detect anomalies early and reduce downtime, which leads to higher efficiency and lower operational costs. As Industry 4.0 matures, CNC machining services will become more data-driven and agile, with greater responsiveness to design changes and production needs.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are gaining traction in CNC machining services. These technologies help optimize tool paths, predict wear and tear, and improve quality control. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from past operations to make recommendations for speed, feed rates, and cutting paths that reduce material waste and improve surface finish.
Moreover, machine learning enhances adaptive control systems in CNC machines, enabling them to self-adjust during machining for better precision. This means fewer human interventions and increased automation throughout the production cycle. In the future, AI-powered CNC machines will likely become standard, capable of learning and evolving over time for continuous improvement.
Advancements in CAD/CAM Software
The role of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software is central to the CNC machining process. Modern advancements in these tools allow for seamless integration between design and manufacturing. Cloud-based platforms are enabling real-time collaboration between engineers, machinists, and designers, speeding up product development cycles.
CAM software is now equipped with AI-assisted features that suggest optimal tool paths and cutting strategies. Additionally, the ability to simulate machining operations before they are executed on the machine significantly reduces errors and material waste. As software becomes more intuitive and powerful, it empowers users to produce complex geometries and high-precision components with greater ease.
Growth of Additive and Hybrid Manufacturing
While CNC machining services are typically associated with subtractive manufacturing, the industry is witnessing a convergence with additive technologies such as 3D printing. Hybrid manufacturing, which combines both subtractive and additive processes, is emerging as a game-changer. This approach allows for greater design flexibility and the creation of intricate parts that would be difficult or impossible to produce with traditional machining alone.
Hybrid machines can build up material using additive techniques and then refine the part using CNC machining. This integration reduces the number of setups, improves part strength, and enhances surface finish. As hybrid manufacturing becomes more mainstream, CNC machining services will expand their capabilities and serve a wider range of industries including aerospace, medical, and automotive.
Expansion of CNC Automation and Robotics
Automation is becoming increasingly prevalent in CNC machining services. From robotic arms loading and unloading parts to automated tool changers and material handling systems, the push toward lights-out manufacturing is well underway. This shift allows manufacturers to run CNC operations 24/7 without human intervention, significantly increasing throughput and reducing labor costs.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are also gaining popularity in CNC environments. These robots work alongside human operators, enhancing productivity while maintaining safety standards. The use of automation not only speeds up production but also improves consistency and quality across batches. As automation technologies become more affordable and accessible, their adoption will continue to grow among small and medium-sized enterprises.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Machining
Sustainability is a growing concern across industries, and CNC machining services are no exception. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices to reduce environmental impact. This includes using biodegradable cutting fluids, recycling metal shavings, and optimizing machining strategies to minimize waste.
Energy-efficient CNC machines are also being developed, incorporating features such as regenerative braking systems and low-power standby modes. Additionally, digital twins and simulations help in planning more efficient production processes, further contributing to resource conservation. As sustainability becomes a top priority, expect CNC machining services to innovate in greener and cleaner ways.
Demand for Customization and On-Demand Manufacturing
Today’s consumers and businesses alike demand greater customization and shorter lead times. CNC machining services are well-positioned to meet these expectations through flexible manufacturing systems. With digital workflows and fast programming capabilities, CNC shops can quickly switch between different product designs and specifications.
On-demand manufacturing allows for small batch production without the need for costly tooling changes. This is particularly valuable for startups, prototyping, and industries that require high precision but low volume, such as medical devices and aerospace components. The trend toward mass customization will only grow stronger, pushing CNC services to become more responsive and adaptable.
Globalization and Distributed Manufacturing Networks
CNC machining services are increasingly becoming part of global supply chains. With advancements in cloud-based manufacturing platforms, companies can now access a global network of CNC service providers. This distributed model reduces dependence on any single location and increases resilience to supply chain disruptions.
Globalization also fosters competition, driving CNC providers to enhance their capabilities, offer faster turnaround times, and maintain consistent quality standards. Customers benefit from a wider range of suppliers and pricing options, while CNC shops gain access to new markets. As digital infrastructure continues to evolve, the global reach of CNC machining services will expand further.
Training, Upskilling, and Workforce Evolution
As CNC machines become more sophisticated, the need for skilled technicians and programmers is on the rise. Traditional machinist roles are evolving into more technical and data-oriented positions. Workers must now understand digital interfaces, AI tools, CAD/CAM software, and automation systems.
To bridge the skills gap, many companies and institutions are investing in training and certification programs. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are also being used for immersive training experiences, helping new workers gain practical experience in a controlled environment. In the years ahead, workforce development will be crucial in ensuring the continued growth and innovation of CNC machining services.
Conclusion
The future of CNC machining services is marked by a fusion of digital innovation, automation, sustainability, and global collaboration. From AI-driven optimization and hybrid manufacturing to smart factories and eco-conscious practices, the industry is undergoing a transformation that promises greater efficiency, precision, and customization.